5 Fascinating Facts About the Norwegian Language

Have you ever wanted to learn the Norwegian language? Are you curious about the origins of this unique and enchanting language?
For those intrigued by the beauty of Scandinavia and its rich cultural heritage, learning the Norwegian language opens up a gateway to a world of fascinating Nordic traditions and captivating landscapes.
In this article, we will explore the Norwegian language, understand its roots, and delve into its unique characteristics. Whether you’re planning a visit to Norway or simply interested in expanding your linguistic repertoire, discovering the Norwegian language is an enriching endeavor.
What Language is Spoken in Norwegian?

Norwegian is the official language of Norway, spoken by the majority of its population. It is one of the North Germanic languages, which are part of the larger Germanic language family.
The other North Germanic languages include Swedish, Danish, Icelandic, and Faroese. While Danish and Swedish have a significant degree of mutual intelligibility, Norwegian maintains its distinct identity and features.
Norwegian has two official written standards: Bokmål and Nynorsk. Bokmål is the more widely spoken standard, and it is based on the Danish written language that was used in Norway during the period of Danish rule (1380–1814). Nynorsk was created in the 19th century as a more Norwegian-based alternative to Bokmål.
Norwegian is a relatively easy language for English speakers to learn, as the two languages share many similarities in vocabulary and grammar.
However, there are some key differences between the two languages. For example, Norwegian uses two genders (masculine and feminine), three cases (nominative, accusative, and genitive), and four verb conjugations.
English is widely spoken in Norway, especially among younger people. However, it is always appreciated when visitors try to speak Norwegian, even if it is just a few basic phrases.
Origins and Influences:
Norwegian has its roots in Old Norse, the language spoken by the Vikings during the Viking Age. Old Norse was a North Germanic language that had a considerable influence on the development of other Germanic languages, including English. Over time, Old Norse evolved into Old Norwegian, which eventually gave rise to the modern Norwegian language we know today.
Characteristics of Norwegian:
As mentioned before Norwegian has two official written forms: Bokmål and Nynorsk.

Bokmål, meaning “book language,” is the more widely used and standardized form, influenced by Danish.
Nynorsk, meaning “New Norwegian,” emerged in the 19th century as a way to preserve and promote Norwegian dialects.
It is based on the rural dialects of western Norway. Both forms are taught in schools, and individuals can choose which one to use in their written communication.
Pronunciation:
Norwegian has a rich set of vowel sounds, which can vary depending on regional dialects. The pronunciation tends to be softer compared to some other Germanic languages, with a melodious quality that reflects the musicality of the Norwegian landscape.
Vocabulary and Grammar:
Norwegian shares similarities with other Germanic languages in terms of vocabulary and grammar. However, it also has its own unique words and expressions, often related to Norway’s natural surroundings, outdoor activities, and maritime culture.
How to Learn the Norwegian Language

If you’re interested in learning Norwegian, there are various resources available, here are some tips for learning Norwegian:
1- Start by learning the basics of Norwegian grammar and vocabulary. There are many online resources and books available to help you with this. Online language courses, textbooks, and language exchange programs can help you acquire the necessary skills.
2- Immerse yourself in the language and Norwegian culture as much as possible. Watching Norwegian movies and TV shows, listening to Norwegian music, and reading Norwegian books and articles can enhance your language-learning journey.
3- Find a language partner or join a Norwegian language class. This will give you the opportunity to practice speaking and listening to Norwegian with other people.
4- Don’t be afraid to make mistakes. Everyone makes mistakes when they are learning a new language. The important thing is to keep practicing and learning from your mistakes.
5- Be patient and persistent. Learning a new language takes time and effort. But if you stick with it, you will eventually reach your goals.
Is Norwegian a Germanic language?
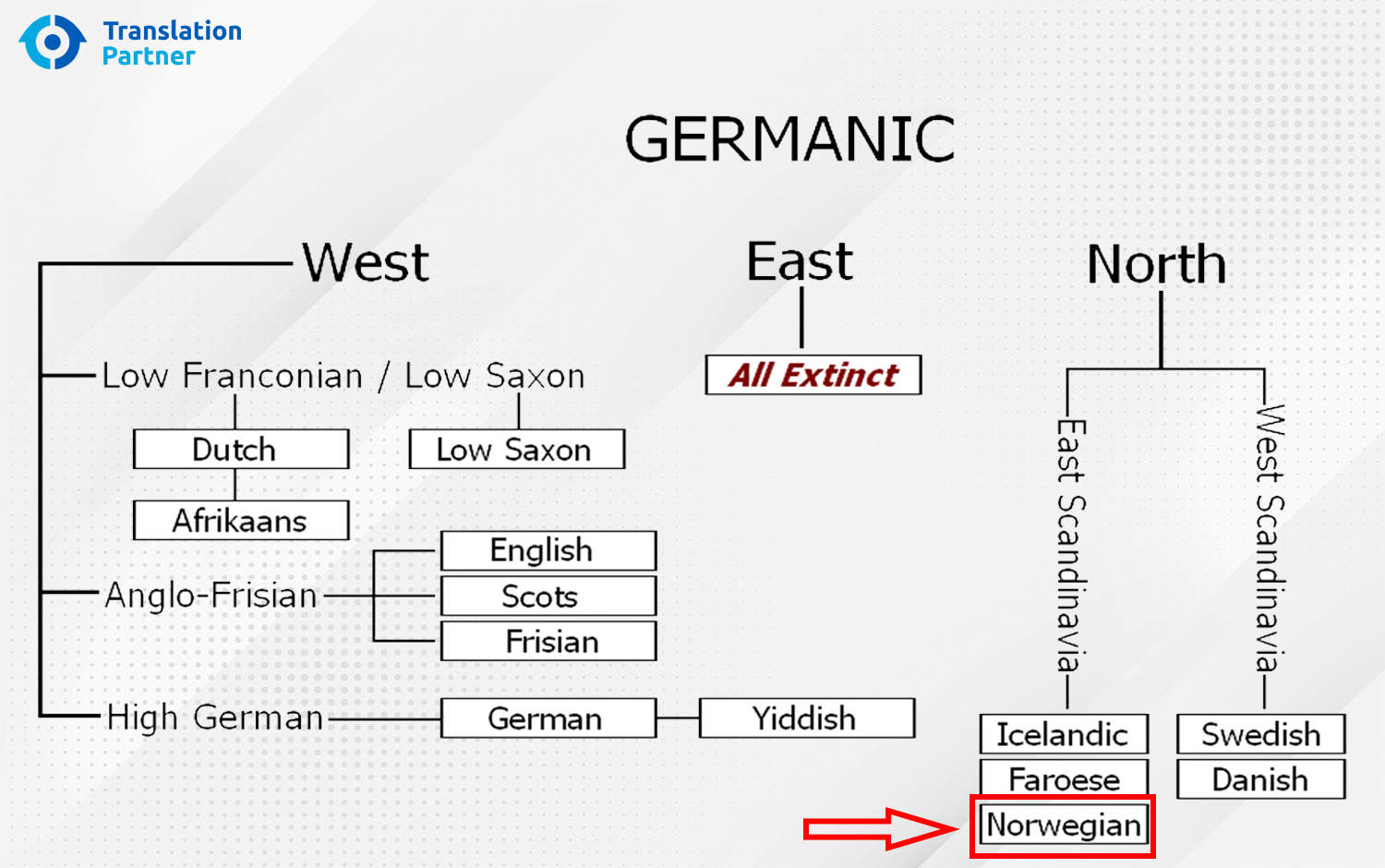
Yes, Norwegian is a Germanic language. It belongs to the North Germanic language branch of the Germanic language tree along with Swedish, Danish, Icelandic, and Faroese. Germanic languages are descended from Proto-Germanic, a language that was spoken in Northern Europe over 2,000 years ago.
Norwegian is closely related to Swedish and Danish, and the three languages are mutually intelligible to a large extent. However, Norwegian also has some unique features, such as the use of two genders (masculine and feminine), three cases (nominative, accusative, and genitive), and four verb conjugations.
Conclusion:
The Norwegian language is a captivating window into the rich heritage and vibrant culture of Norway. As a North Germanic language, Norwegian has its own distinct identity, influenced by its historical roots and regional dialects.
Whether you choose to learn Bokmål or Nynorsk, embracing the Norwegian language opens up opportunities to connect with a welcoming community and explore the breathtaking landscapes of this Nordic nation. So, embark on your linguistic adventure and discover the joys of learning the Norwegian language.
