Now and then, I receive the same question from different clients we work with: “Which dialect of Arabic should we use in our translation project? Or “Can we use the translation in all the Arab countries?” or “What is the difference between Arabic spoken in Egypt and Saudi Arabia?”
Arabic is spoken in 22 countries, covering almost 12.9 million square kilometers. This is a huge area with different cultures and business challenges.
So, customers have the right to know how they can use their translations to avoid any damage to their reputation if something fails to work with the translation, or at least to save costs if they can use the translation across 22 countries.
In this article, I will explain different variants of the Arabic language and how they can affect your next translation project. Let’s start with an answer to this question.
How many dialects does the Arabic language have?
You can consider that each Arab country has its own dialect. I would go so far as to say that inside every country, you may find different sub-dialects. However, you only need to know the three main variants of Arabic when it comes to translation work.
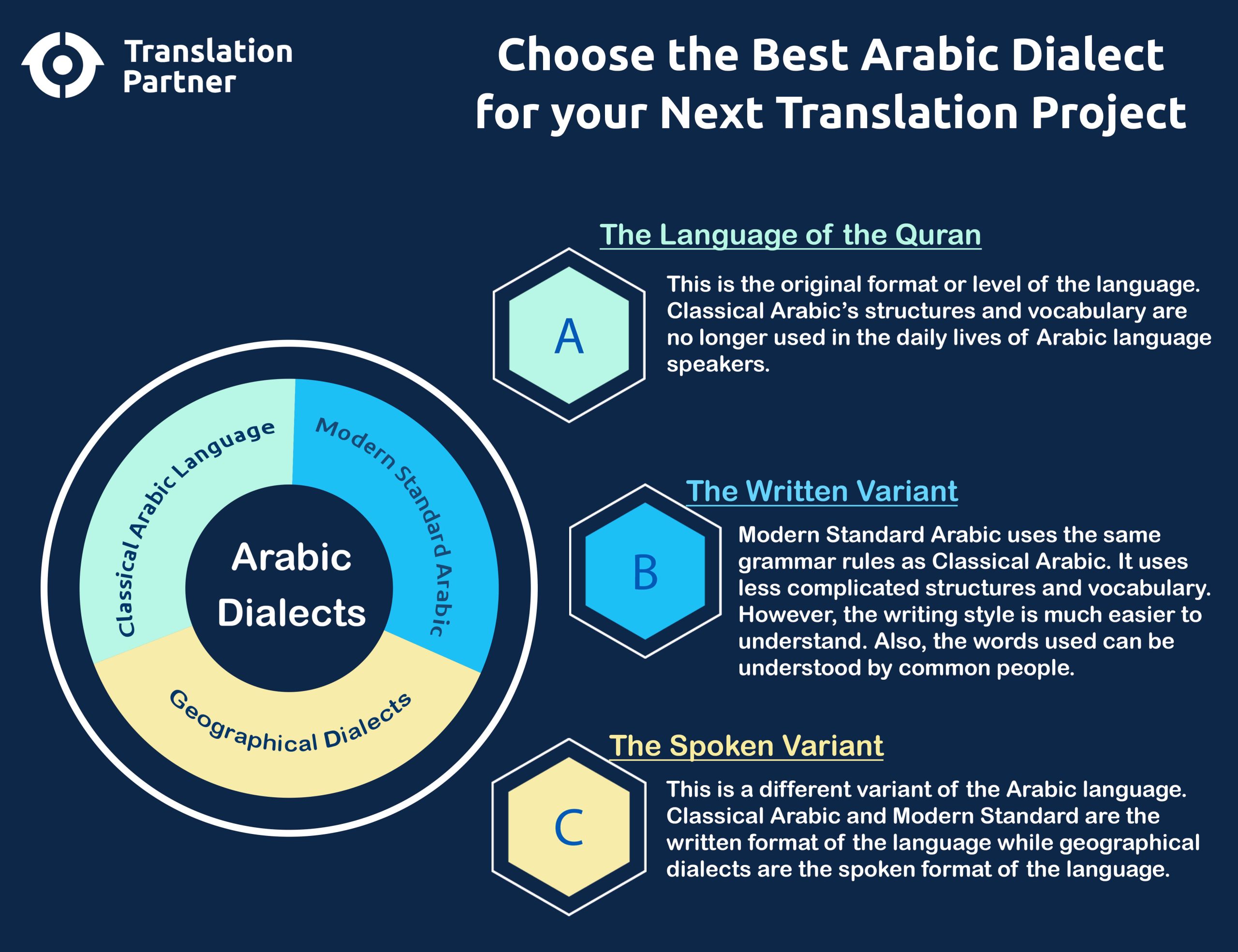
A. Classical Arabic Language: The Language of the Quran
What it is:
This is the original format or level of the language. Classical Arabic structures and vocabulary are no longer used in the daily lives of Arabic language speakers.
Not every educated person in the Arab world can read Classical Arabic. It is complicated and requires deep study to understand. Many times, I have to use a dictionary to understand it, even though I am a native Arabic speaker.
Where it is used:
This is the linguistic format used in the Quran and recitations of the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be Upon Him), along with the classic poems of Arabic literature. Also, it is the language of old books written in the first 300-600 years of Islam.
It is not common to use Classical Arabic to write legal articles or official documents. In the 19th and 20th centuries, some writers used to write using structures taken from Classical Arabic, but their articles were very hard for common people to read.
Personal Note:
Although I am a native Arabic speaker, it is really hard for me to read Arabic texts written in Classical Arabic. Many times, I have to use a dictionary to understand the meaning of the words. Writers like Abbas El Aqad or Mostafa Al Rafee used this level of Arabic to write their articles and books in the 20th century, and we study it in schools. I remember how we suffered to understand their writings.
B. Modern Standard Arabic: The Written Variant
What it is:
This is the modern format of Classical Arabic. It uses less complicated structures and vocabulary. It seems that with the expansion of Arab culture and rule, many countries had an effect on the changes to the language that generated this level of the Arabic language over time.
Modern Standard Arabic uses the same grammar rules as Classical Arabic. However, the writing style is much easier to understand. Also, the words used can be understood by common people.
Where it is used:
Modern Standard Arabic is the language of publications in all Arab countries. It is used in newspapers, magazines, books, official documents, business communication, and legal documents.
Wherever you do business in the Arab world, you can communicate using Modern Standard Arabic as long as your communication is in the written format. If you will communicate verbally, you need to use the spoken dialect of the country you are in.
Personal Note:
Modern Standard Arabic is the level I used to connect with native Arabic speakers in countries like Tunisia, Morocco, and Algeria. Yes, we are all Arabs, but the spoken level is totally different. So, it is easier for us to communicate in Modern Standard Arabic as it is understood in all Arab countries. For no native speakers, it is essential to understand Modern Standard Arabic to communicate well with more Arabs.
C. Geographical Dialects: The Spoken Variant
What it is:
This is a different variant of the Arabic language. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard are the written formats of the language, while geographical dialects are the spoken format of the language. As I mentioned, every Arab country has a unique spoken dialect.
The sounds and words of the dialect depend on the country you live in. The funny thing is, some native Arabic speakers may not understand the dialects of each other if they are from different Arab countries. They may speak Modern Standard Arabic to reach a common ground.
Where it is used:
It is the language variant used in daily conversations, in the market, over the phone, with colleagues, in movies, and when negotiating in a spoken context. If you live in any Arab country, you need to learn its dialects.
Dialects are important if you communicate verbally a lot with your business partners. You will seem more professional and easier to work with.
Personal Note:
Egyptian spoken dialect is more common than any other spoken Arabic dialects. This is due to the spread of Egyptian movies and songs. You will find many Arabs who know Egyptian jokes and proverbs. Even in the western countries where Arabs live, you will hear the sound of the famous Egyptian singer Om-Kolthoum in every cafe and restaurant you visit.
Which Variant is the Best for your Next Translation Project?
There are different factors to be considered to deciding when choosing the appropriate Arabic dialect in translation projects. You need to ask, “Why do I need this translation?” This will make it easy for you to choose the right dialect.
Request A FREE Translation Cost Estimate!
Click the below button and request a free price quote for translation services—no commitment on your side.
If the translation will be used in a formal context, like writing an agreement signature, a company policy, or a medical report, Modern Standard Arabic will be used. It is the variant used in both government and private written documents. Also, using Modern Standard Arabic enables you to use the same translation for almost all the Arab countries, which saves you time and effort in the future.
If you need the translation for advertising purposes, this can be tricky. The best way to deliver your marketing message to your customers in the Arab world is to use the local spoken dialect. If this is the case, you need to use a local translator who speaks and understands the dialect of this specific country. For example, if your translation will be used in a TV advertisement for the Egyptian people, you need to hire an Egyptian translator and ask him/her to use the local Egyptian dialect.
As you can see, the purpose of the translation can have a great effect on choosing the right Arabic dialect. You need to communicate that clearly with your translation team. This will help to assign the translation project to a qualified translator and to avoid losing money and energy if the translation turns out to be unusable.
Additional Reading: What language is spoken in Dubai?
Conclusion
Arabic is a widely spoken language across different countries with unique regional cultures. You need to be cautious when working on an Arabic translation project. Preparing beforehand and providing clear instructions to your team will streamline the translation phase.
In most cases, Modern Standard Arabic is the best choice as it is the written format of the language. It is used in business, official, and personal papers. If you are confused, ask for a translation in Modern Standard Arabic.

